Cell energy
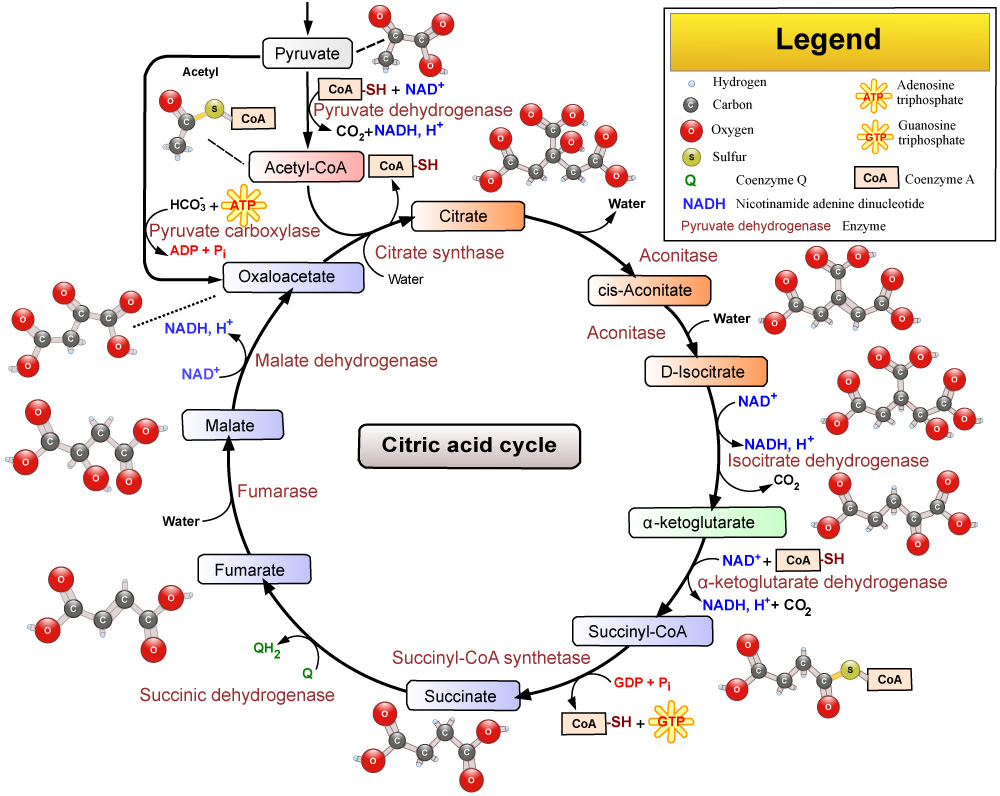
A part of the energy released during the breakdown of glucose in the cells is stored in the form of high-energy phosphate, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which thus provides the energy necessary for the functioning of cells. The NAD+ coenzyme, which is the key to energy production and transport, is also essential for the creation of ATP.
In old age, the number of energy-producing mitochondria in cells decreases and less NAD+ is produced. In many cases, due to the inflammatory processes that develop in old age, the body’s regenerative processes and immune system are exposed to continuous “load”, which would require more energy. However, since energy production and energy transport can provide the energy requirement in an increasingly limited way, important cellular functions are lost as a result. The goal is therefore to restore the number and function of mitochondria and to replace missing molecules, such as NAD+, which are essential for the body’s energy production.
The amount of NAD+ in the body can be significantly increased by taking Nicotinamide Riboside (NR). From these molecules, the body produces NAD+, which can thus contribute to restoring the body’s energy production.
What is NAD+?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or NAD+ is a coenzyme molecule that plays an important role in cellular metabolism, a component of our bodies so important that we could not live without it.
It plays a role in energy transport, regulating the sleep-wake cycle, and repairing damaged DNA, among other functions, but lower levels of NAD+ are also associated with aging in people.
The development of MyCellen is a product to maintain NAD+ levels. A pack of MyImmuNAD+ contains 30 capsules, which corresponds to a monthly dose. It is recommended to take one capsule per day regularly in the morning to maintain appropriate NAD+ levels in the body.

MyImmuNAD+ 3 Boxes
The dietary supplement MyImmuNAD+ contains Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), Vitamin D3, Resveratrol, Quercetin and Coenzyme Q10.
Packaging: 30 capsules
